Generative AI is perhaps one of the most promising and exciting innovations, and it forms a significant trend in technology today. From images to human-like writing, music generated, and designs generated, Generative AI is poised against the boundaries of what machines can or cannot do. So, what is Generative AI, and how does it work?
Understanding Generative AI
Generative AI represents a form of AI that generates brand-new content. Unlike traditional AI which mostly exists to reflect on what has already been produced and make predictions from such data, generative AI is concerned with creating entirely new data, not copying data created in the past. An example may include text, images, audio, and videos.
It fundamentally consists of models mostly trained on really big data, learning patterns, styles, and structures of the data used to model to produce quite new data that would indeed look analogous to the original data in very significant ways.
Now What is Generative AI and why it matters??
The magic lies in the construction of Generative AI and its architecture; in this case, neural networks like Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Transformer models (e.g., GPT, BERT).
Generative Adversarial Networks
The two parts of GANs are:
- Generative Content: A generator that creates or generates fresh content.
- Discriminator: An evaluator that assesses it to determine whether the content is authentic or not.
These networks bring together the feedback loop to help them build over time until the generator produces outputs that look highly realistic.
Transformers
Transformers give birth to artificial works like those found in Open AI’s GPT models. The basic mechanism involves predicting the next computation- word, image pixel, or data point in a sequence.
It makes use of self-attention to comprehend how different elements of the input correspond with one another.
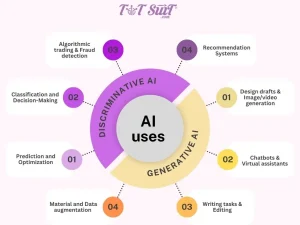
Applications of Generative AI
The possibilities have no limits in any industry. Some most notable ways include:
- Generating content: Writing articles, generating captions, and producing ideas for creative projects.
- Art and Design: Digital artwork, animation, or graphics production.
- Healthcare: Simulation of drug molecules, prediction of protein structures.
- Entertainment: Realistic characters and environments for games and films.
- Personalization: Such as in forming recommendations and responses in chatbots.
Benefits and Challenges
Benefits:
- Creativity Enhancement: Human experimentation and innovation have been accelerated so that they may do it more quickly.
- Efficiency: Automates the lengthy and tedious creative processes.
- Accessibility: Access to sophisticated tools by non-experts.
Challenges:
- Bias from the Data: If the training data were biased, such bias would show up in what was generated.
- Ethics: This raises questions about the unethical use of such generative AI, such as in deepfakes and fake news.
- Intellectual Property Rights: Who owns the rights to creations made by AI?
The futur of Generative AI
Generative AI is set to be one of the icons of change in the world. Furthermore, it will enhance its ability to augment human creativity and solve highly complex problems. With this, it will become the driver of innovation and, thus, take the future of technology by storm. As one possibly pours into the capacity of such technology, ethical and societal implications in the use of generative AI are equally to be addressed for responsible use.





Comment 1